ARP POISONING ATTACK
- What is ARP ?
The Address Resolution
Protocol (ARP) is a computer networking protocol for determining a
network host's hardware address (MAC) or link layer when only its
Internet Layer (IP) or Network Layer address is known. In fact it’s a IP
to MAC mapping.
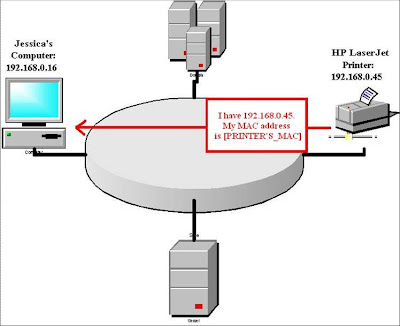
Broadcast ARP Request:
Jessica,
the receptionist, tells Word to print the latest company contact list.
This is her first print job today. Her computer (IP address
192.168.0.16) wants to send the print job to the office's HP LaserJet
printer (IP address 192.168.0.45). So Jessica's computer broadcasts an
ARP Request to the entire local network asking, "Who has the IP address,
192.168.0.45?"
Unicast ARP Reply:
All
the devices on the network ignore this ARP Request, except for the HP
LaserJet printer. The printer recognizes its own IP in the request and
sends an ARP Reply: "Hey, my IP address is 192.168.0.45. Here is my MAC
address: 00:90:7F:12:DE:7F"
- ARP Poisoning:
Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP) spoofing, also known as ARP poisoning or ARP
Poison Routing (APR), is a technique used to attack an Ethernet wired or
wireless network. ARP Spoofing may allow an attacker to sniff data
frames on a local area network (LAN), modify the traffic, or stop the
traffic altogether.
The
ability to associate any IP address with any MAC address provides
hackers with many attack vectors, including Denial of Service (DoS), Man
in the Middle, and MAC Flooding.
- Man in the Middle Attack (MIMA):
A hacker can exploit ARP Cache Poisoning to intercept network traffic between two devices in your network.
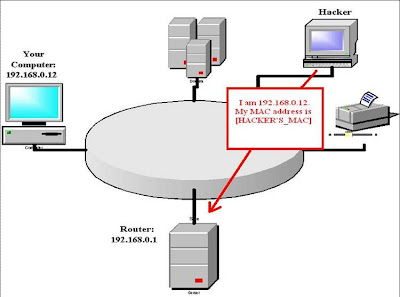
Attack Stage-1:
The
hacker wants to see all the traffic between your computer,
192.168.0.12, and your Internet router, 192.168.0.1. The hacker begins
by sending a malicious ARP "reply" (for which there was no previous
request) to your router, associating his computer's MAC address with
192.168.0.12.
Attack Stage-2:
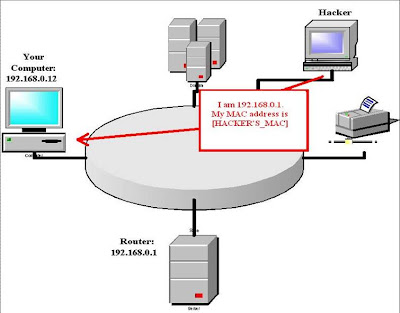
Now
your router thinks the hacker's computer is your computer. Next, the
hacker sends a malicious ARP reply to your computer, associating his MAC
Address with 192.168.0.1

Attack Stage-3:
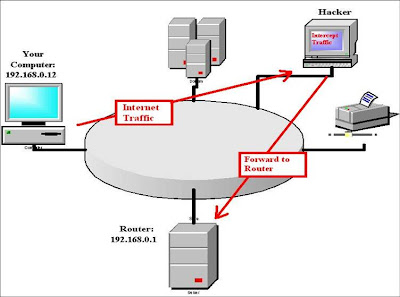
Now
your machine thinks the hacker's computer is your router. Finally, the
hacker turns on an operating system feature called IP forwarding. This
feature enables the hacker's machine to forward any network traffic it
receives from your computer to the router.

- ARP Poisoning Tool:
Ettercap
is a suite for man in the middle attacks on LAN. It features sniffing
of live connections, content filtering on the fly and many other
interesting tricks. It supports active and passive dissection of many
protocols and includes many feature for network and host analysis.

Download ETTERCAP from here.

- Protection:
1.
Arpwatch is a computer software tool for monitoring Address Resolution
Protocol traffic on a computer network. Network administrators monitor
ARP activity to detect ARP spoofing.
2. Arping
is a computer software tool that is used to discover hosts on a computer
network. The arping tool is analogous in function to ping, which probes
hosts using the Internet Control Message Protocol at the Internet Layer
(OSI Layer 3).
3. Capsa Network Analyzer
(Packet Sniffer) is an easy-to-use Ethernet network analyzer (aka.
packet sniffer or protocol analyzer) for network monitoring and
troubleshooting purposes.

Happy Hacking...Enjoy...
For educational purpose only...Do not misuse it..
Fore More -::- about dealing with cash memory (view, refresh, clear ) click here
For educational purpose only...Do not misuse it..
Fore More -::- about dealing with cash memory (view, refresh, clear ) click here








