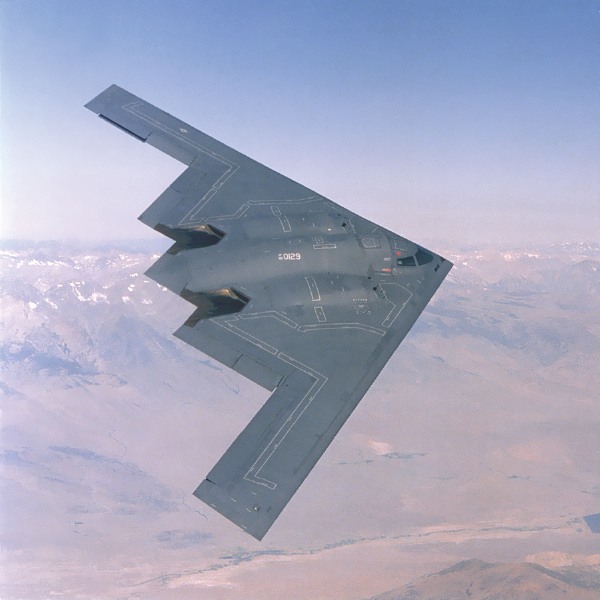
A stealth fighter is just that we cannot detect its presence with radar.The observer can rely on the time difference from emission to reception to locate the enemy fighter. Aircrafts usually have a curved surface in order to minimize air resistance in flight. Thus, electromagnetic waves impinged in any direction will be partly reflected to their original direction, leading to a large signal on the radar detector.
Work on stealth has its roots in long-standing efforts to reduce the visibility of military aircraft through camouflage paint schemes. As electronic sensors have replaced the eyes of pilots as the primary means of tracking other aircraft, more intricate means of defense were needed.

Often the use of special materials (typically
carbon, carbon fibre composites, or
magnetic ferrite-based substance) renders aircraft invisible to radar, stealth reduces the ability of an opponent’s sensors to detect, track and attack an aircraft.
 A variety of technologies are may be combined in order to make itself “invisible” to radar
A variety of technologies are may be combined in order to make itself “invisible” to radar. These technologies include a smooth surface, “flying wing” design, radar absorbent materials (RAM) and electronic countermeasures (ECM).
Radar absorbent material (RAM): when radar impacts radar absorbent material, the energy acts as though it “sees” infinite free space instead of a boundary. The absorbed electromagnetic energy is dissipated as heat and very little energy is reflected.
Disadvantages: additional weight, expense, heating problems and aerodynamic drag.
 Electronic countermeasures (ECM):
Electronic countermeasures (ECM): are referred to as any electronic effort intended to disturb normal radar operation. The defence may utilize ECCM to overcome and mitigate the effects of ECM on the radar.

To understand, why a reflexed airfoil is able to provide longitudinal stability to a wing, two things are important:
- Total Force and Moment: the pressure forces, which act on the surface of each wing section, can be replaced by a single total force and a single total moment. Both act at the quarter-chord point (c/4) of the airfoil. When the angle of attack changes, the moment stays nearly constant, but the total force changes.
- Center of Gravity : When the angle of attack of a plane changes, the plane rotates (pitches) around its center of gravity.
The planes low radar cross section (RCS) reduces the range at which ground-based and air-based radars can detect the aircraft. String reel target manipulation systems are used to support targets for
low frequency
RCS measurements.The RAM absorbs most of a radar’s signal, and the aircraft’s wing-shaped and rounded design redirects much of the remaining power away from the radar source.
RADAR ( Radio Direction Finding)

A radio transmitter is a device that oscillates an electrical current so the voltage goes up and down at a certain frequency. This electricity generates electromagnetic energy, and when the current is oscillated, the energy travels through the air as an
electromagnetic wave. A transmitter also has an amplifier that increases the intensity of the electromagnetic energy and an antenna that broadcasts it into the air.
A radio receiver is just the reverse of the transmitter: it picks up electromagnetic waves with an antenna and converts them back into an electrical current.
Radar is the use of radio waves to detect and monitor various objects.

The radar device emits a concentrated radio wave. Radio waves move through the air at a speed of light (
c )so the radar device can calculate how far away the object is based on how long it takes the radio signal to return.

The other elements of air defense detection and tracking are
infrared (IR) light, electro-optical (EO) sensors.
IR light is an electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light. Infrared light has a range of wavelengths, just like visible light has wavelengths that range from red light to violet.
 Limitations
Limitations
Some of the materials used require special and costly maintenance. The maneuverability of an aircraft can be compromised by the introduction of stealth design features. As was the case with the F-117A.

FLIRS (Forward looking infrared System)
FLIRs make pictures from heat, not visible light. Heat (also called infrared, or thermal energy) and light are both parts of the electromagnetic spectrum, but a camera that can detect visible light won’t see thermal energy, and vice versa.

The wavelength of infrared that FLIRs detects differs from that of night vision, which operates in the visible light and near infrared ranges (0.4 to 1.0 micrometres). Stealth aircraft may rely on an airborne laser radar, although such a sensor may prove of limited utility in bad weather. There are limits to the utility of stealth techniques. Since the radar cross-section (RCS) (
radar cross section is the measure of a target’s ability to reflect
radar signals in the direction of the radar receiver) of an aircraft depends on the angle from which it is viewed.

Stealth aircraft are designed to minimize their frontal RCS. But
it is not possible to contour the surface of an aircraft to reduce the RCS equally
in all directions, and reductions in the frontal RCS may lead to a larger RCS from above. Thus while a stealth aircraft may be difficult to track when it is flying toward a ground-based radar or another aircraft at the same altitude, a high-altitude airborne radar or a space-based radar may have an easier time tracking it. Another limitation of stealth aircraft is their vulnerability to detection by bi-static radars.

Programs
F-117 (Nighthawk) — The F-117 first flew in 1983. The original F-117 program envisioned over 100 aircraft, but soaring costs (each aircraft costs over $100 million), performance problems (several of the aircraft have crashed in training flights), limited payload (the aircraft can carry only two 900 Kg laser guided bombs internally), and the lack of a clearly defined mission all contributed to the curtailment of the program.
 ATB (Advanced Technology Bomber)- B-2
ATB (Advanced Technology Bomber)- B-2 — The Stealth Bomber project was first announced in 1980. In November 1988, the B-2 has been the focus of criticism of the growing cost of the program/project.

The B-2 will be the most expensive aircraft ever procured!
Acoustic Detection
How owls developed stealth technology !!!?
The owl's wing is broad and rounded compared to that of other birds, which makes for less flapping, and a quieter ride through the air. That reduces some sound, but an owl is quiet even compared to other birds when they glide. It's more than just a difference in wing measurements. It's the fact that owls are fully upholstered in order to maintain silence.

The inside of music studios, concert halls and movie theaters is covered with blocks of fabric. These muffle sound and prevent echoing. An owl's hard surfaces, specifically its legs and feet, are covered with soft feathered that muffle noise.
It's the wing feathers that are really counter intuitive, though. Most people, when designing something that makes little noise, will make it as sleek and rounded as possible. That turns out to be a mistake. A sleek, streamlined thing won't have any extra parts banging off each other or creaking in the wind. As we've seen before, though, it will have turbulence. Turbulence is moving air and moving air makes noise.
On the front of the owl's wing are feathers shaped like combs. The teeth of the combs lined the leading edge of the wing, and like the bumps on a whale's flukes, break up the stream of air moving over the wing. At the other side of the wing, the feathering is uneven, creating a fringe-like back edge. The combination takes the air that would all splash off the wing at the same time, and instead lets it out in isolated dribbles.

The result? Evolutionary advantage. Silent death. The ninjas of the animal world. All kinds of ancient myths. Supernatural mystery. And David Bowie. I don't know how the last one fits in, either.
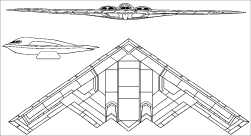
B-2 Stealth Bomber
Currently in action in Libya, we take a look at how this formidable member of the United States Air Force works
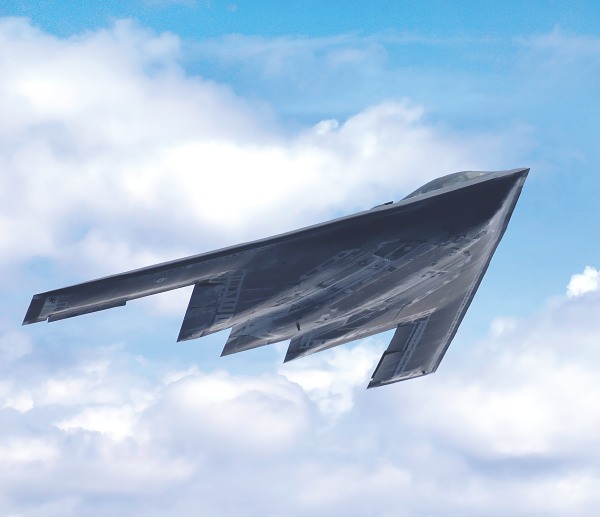

The ‘flying wing’ shaped Stealth Bomber (nicknamed ‘Spirit’) is a unique aircraft that’s designed to make it as invisible as possible. Its shape means there are very few leading edges for radar to reflect from, reducing its signature dramatically. This is further enhanced by the composite materials from which the aircraft is constructed and the coatings on its surface. These are so successful that despite having a 172-foot wingspan, the B-2’s radar signature is an astounding 0.1 square metres.
The B-2’s stealth capabilities, and aerodynamic shape, are further enhanced by the fact its engines are buried inside the wing. This means the induction fans at the front of the engines are concealed while the engine exhaust is minimised. As a result, the B-2’s thermal signature is kept to the bare minimum, making it harder for thermal sensors to detect the bomber as well as lowering the aircraft’s acoustic footprint.
The design also means the B-2 is both highly aerodynamic and fuel efficient. The B-2’s maximum range is 6,000 nautical miles and as a result the aircraft has often been used for long-range missions, some lasting 30 hours and in one case, 50. The B-2 is so highly automated that it’s possible for a single crew member to fl y while the other sleeps, uses the lavatory or prepares a hot meal and this combination of range and versatility has meant the aircraft has been used to research sleep cycles to improve crew performance on long-range missions. Despite this, the aircraft’s success comes with a hefty price tag. Each B-2 costs $737 million and must be kept in a climate-controlled hangar to make sure the stealth materials remain intact. These problems aside though, the Spirit is an astonishing aircraft, even if, chances are, you won’t see one unless the pilots want you to…
Inside the Spirit
The B-2 is an unusual combination of complexity and elegance, the entire airframe built around the concept of stealth and focused on making the aircraft as hard to detect as possible.
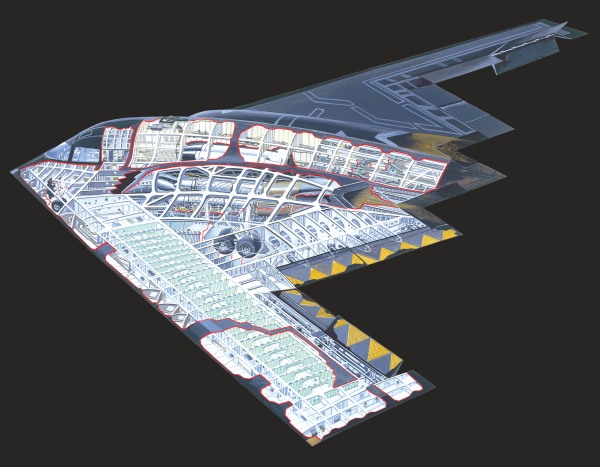 Windows
Windows
The B-2′s windows have a fine wire mesh built into them, designed to scatter radar.
Composite materials
Any radar returns are reduced by the composite materials used, which further deflect any signals.
Carbon-reinforced plastic
Special heat-resistant material near the exhausts mean the airframe absorbs very little heat.
Rotary launch assembly (RLA)
The RLA allows the B-2 to deploy different weapons in quick succession.
Bomb rack assembly (BRA)
The bomb rack assembly can hold up to eighty 500lb bombs.
Air Intakes
To further reduce the B-2′s signature, the engine intakes are sunk into the main body.
 Landing gear doors
Landing gear doors
The landing gear doors are hexagonal to further break up the B-2′s radar profile.
Crew compartment
The B-2 carries two crew, a pilot and a mission commander with room for a third if needed.
Flying wing
The B-2′s shape means it has very few leading edges, making it harder to detect on radar.
Fly-by-wire
The B-2′s unique shape makes it unstable, and it relies on a computer to stabilize it and keep it flying.
Engines
The B-2′s four General Electric F118s don’t have afterburners as the heat these generate would make the aircraft easier to detect. (IR signature)
The Statistics
 Manufacturer
Manufacturer
Northrop Grumman
Armament